Impact Radius
Impact Radius helps you analyze changes and identify downstream impacts at the column level.
While dbt provides a similar capability using the state selector with state:modified+ to identify modified nodes and their downstream dependencies, Recce goes further. By analyzing SQL code directly, Recce enables fine-grained impact radius analysis. It reveals how changes to specific columns can ripple through your data pipeline, helping you prioritize which models—and even which columns—deserve closer attention.
Usage
Show impact radius
-
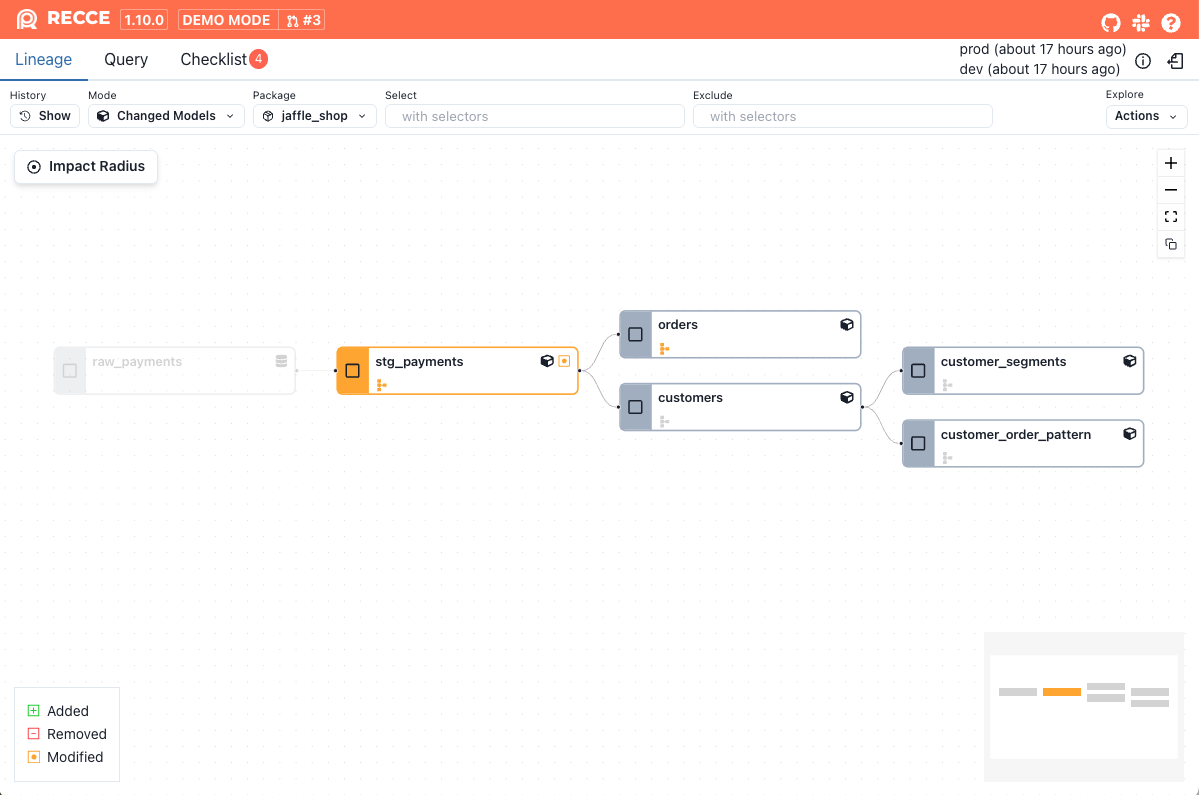
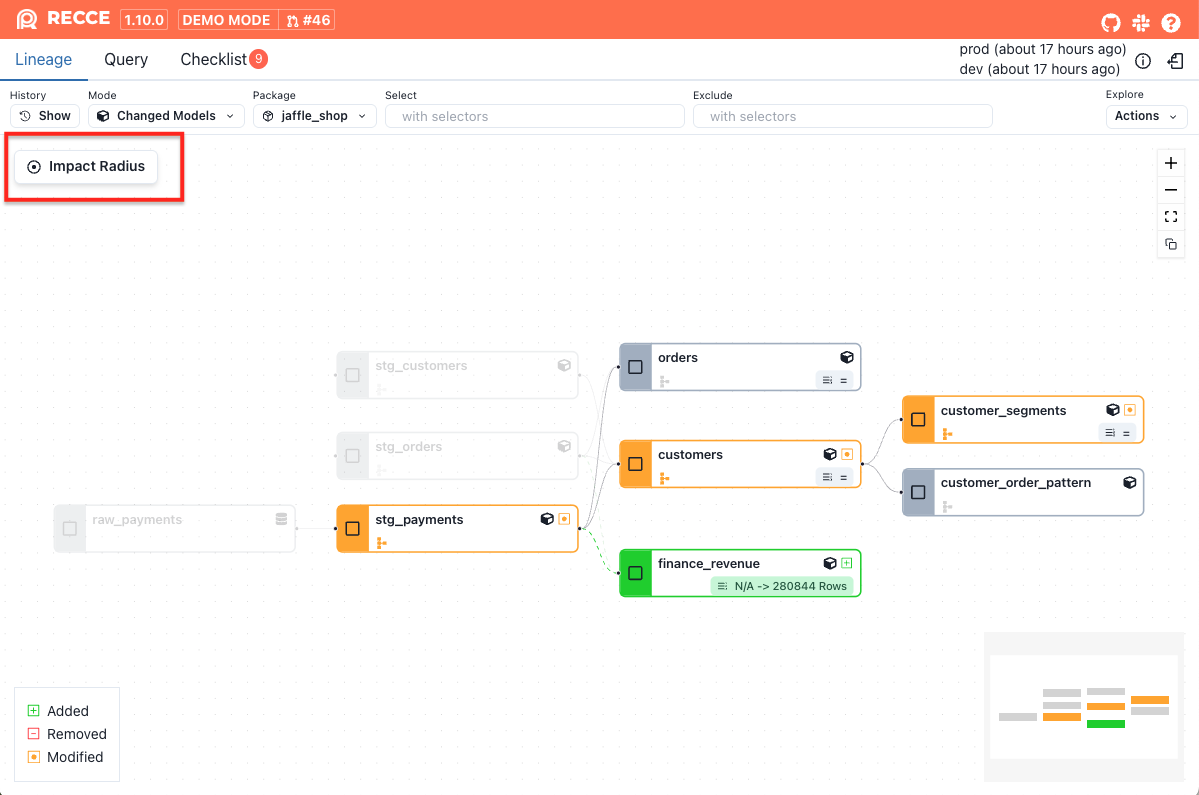
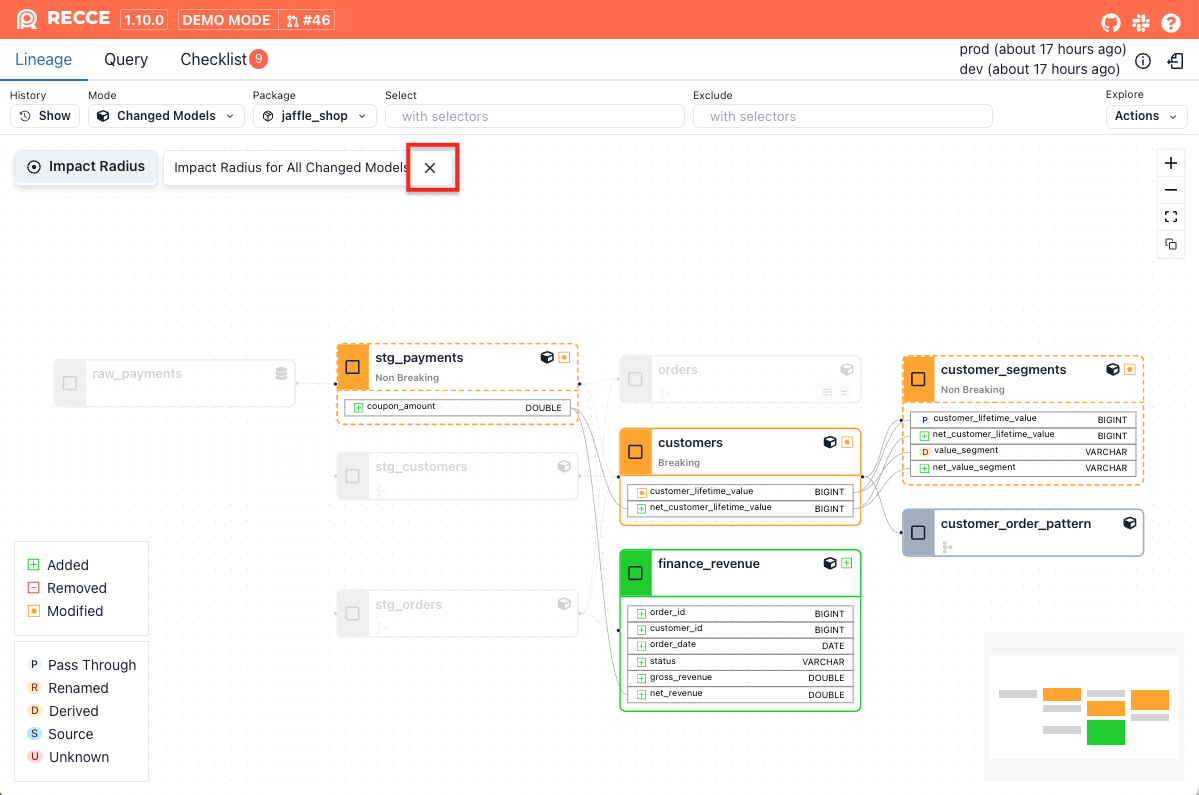
Click the Impact Radius button in the upper-left corner.
-
The impact radius will be displayed.
-
To exit impact radius view, click the close button in the upper-left corner.
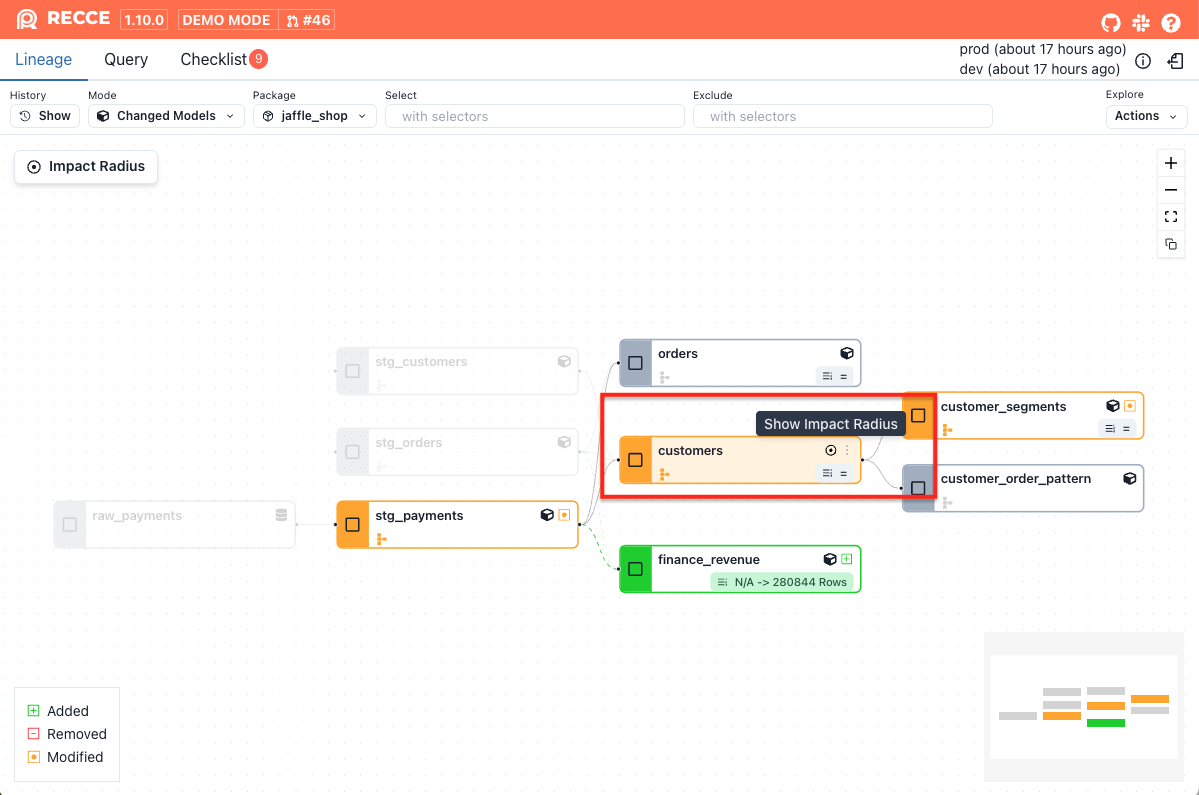
Show impact radius for a single changed model
-
Hover over a changed model, then click the target icon or right-click the model and click the Show Impact Radius
-
The impact radius for this model will be displayed.
-
To exit impact radius view, click the close button in the upper-left corner.
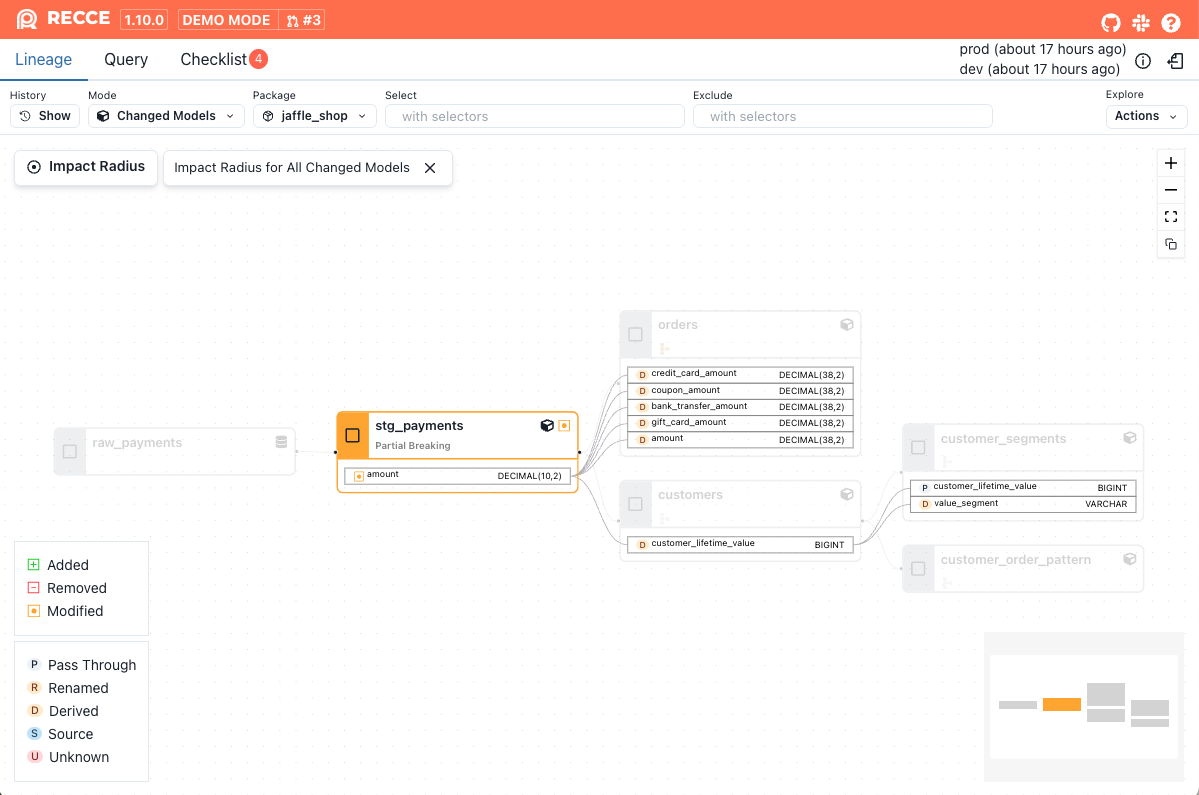
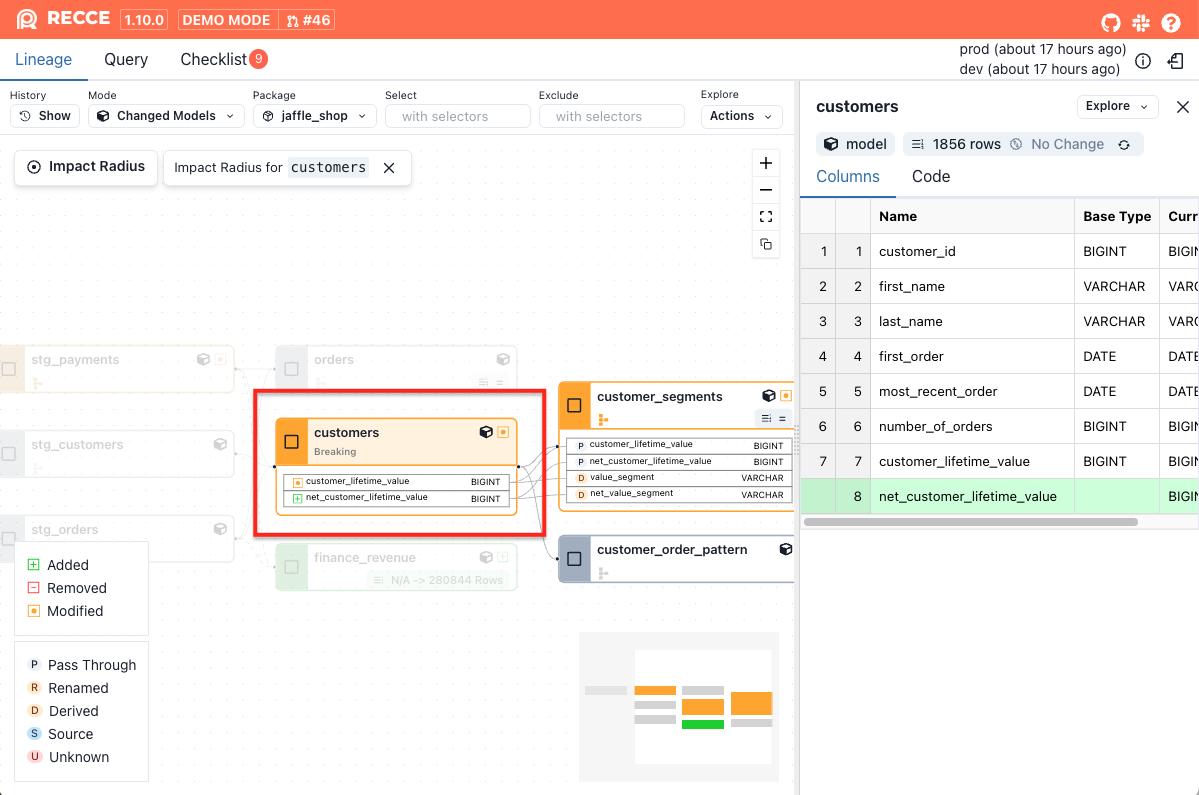
Impact Radius of a Column
The right side of the Column-Level Lineage (CLL) graph represents the impact radius of a selected column. This view helps you quickly understand what will be affected if that column changes.
What does the impact radius include?
- Downstream columns that directly reference the selected column
- Downstream models that directly depend on the selected column
- All indirect downstream columns and models that transitively depend on it
This helps you evaluate both the direct and downstream effects of a column change, making it easier to understand its overall impact.
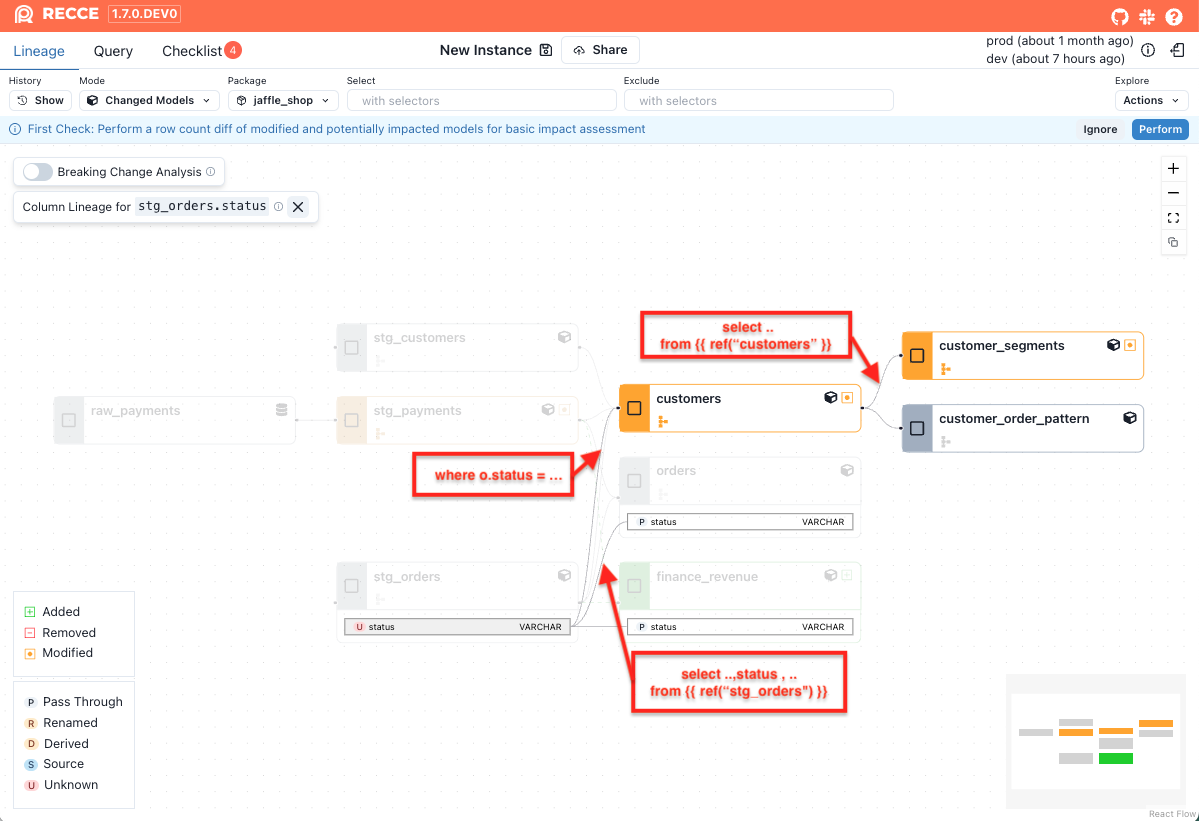
Example: Simplified Model Chain
Given the following models, here's how changes to stg_orders.status would impact downstream models:
-- stg_orders.sql
select
order_id,
customer_id,
status,
...
from {{ ref("raw_orders") }}
-- orders.sql
select
order_id,
customer_id,
status,
...
from {{ ref("stg_orders") }}
-- customers.sql
select
c.customer_id,
...
from {{ ref("stg_customers") }} as c
join {{ ref("stg_orders") }} as o
on c.customer_id = o.customer_id
where o.status = 'completed'
group by c.customer_id
-- customer_segments.sql
select
customer_id,
...
from {{ ref("customers") }}
The following impact is detected:
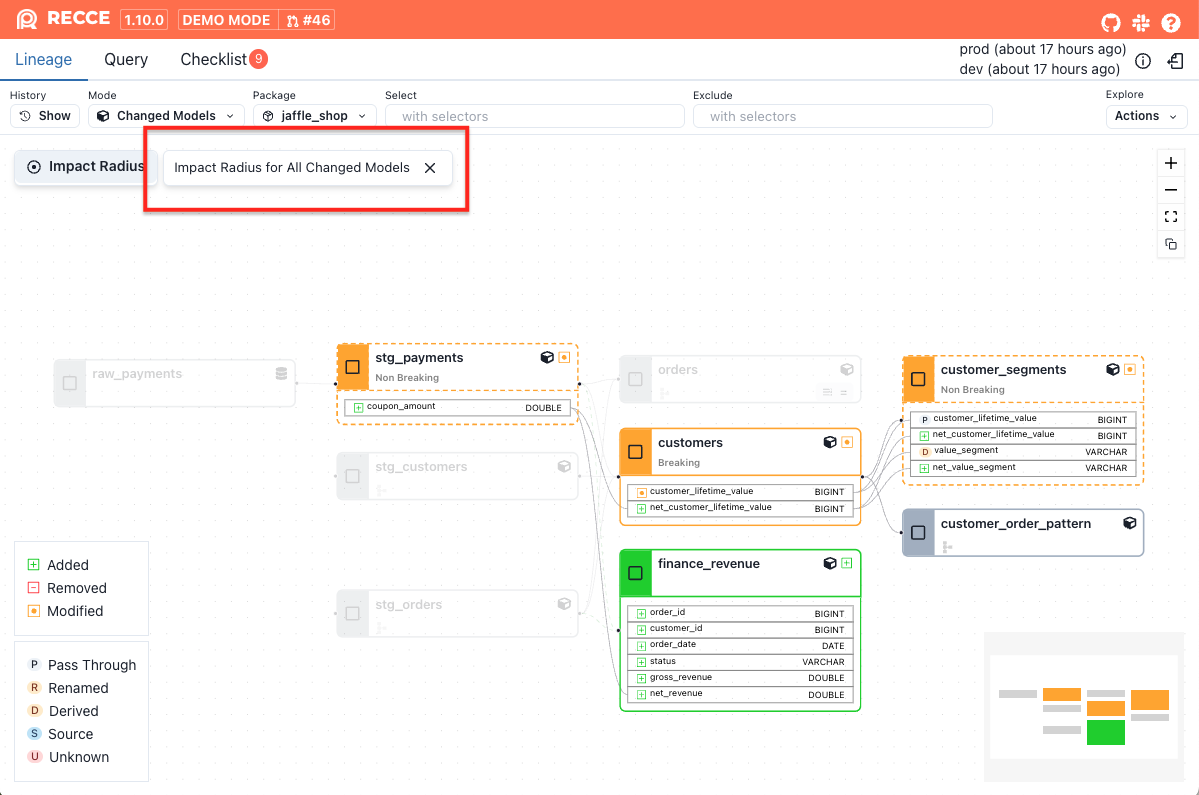
-
orders: This model is partially impacted, as it selects the
statuscolumn directly fromstg_ordersbut does not apply any transformation or filtering logic. The change is limited to thestatuscolumn only. -
customers: This model is fully impacted, because it uses
statusin a WHERE clause (where o.status = 'completed'). Any change to the logic instg_orders.statuscan affect the entire output of the model. -
customer_segments: This model is indirectly impacted, as it depends on the
customersmodel, which itself is fully impacted. Even thoughcustomer_segmentsdoes not directly referencestatus, changes can still propagate downstream via its upstream dependency.
How it works
Two core features power the impact radius analysis:
Breaking Change Analysis classifies modified models into three categories:
- Breaking changes: Impact all downstream models
- Non-breaking changes: Do not impact any downstream models
- Partial breaking changes: Impact only downstream models or columns that depend on the modified columns
Column-level lineage analyzes your model's SQL to identify column-level dependencies:
- Which upstream columns are used as filters or grouping keys. If those upstream columns change, the current model is impacted.
- Which upstream columns a specific column references. If those upstream columns change, the specific column is impacted.
Putting It Together
With the insights from the two features above, Recce determines the impact radius:
- If a model has a breaking change, include all downstream models in the impact radius.
- If a model has a non-breaking change, include only the downstream columns and models of newly added columns.
- If a model has a partial breaking change, include the downstream columns and models of added, removed, or modified columns.